XXVII.1.5 It is said to be statistically impossible that something as complex as an organism could be the result of a random process of evolution
Statistical reasons for the impossibility of the formation of an organism would be valid only for a single-step emergence.However, the theory of natural selection assumes the gradual, multi-step formation of living systems.The differences can best be illustrated using the well-known thought experiment (Fig. XXVII.1).If we sit a troop of apes down to typewriters and teach them to press the keys,
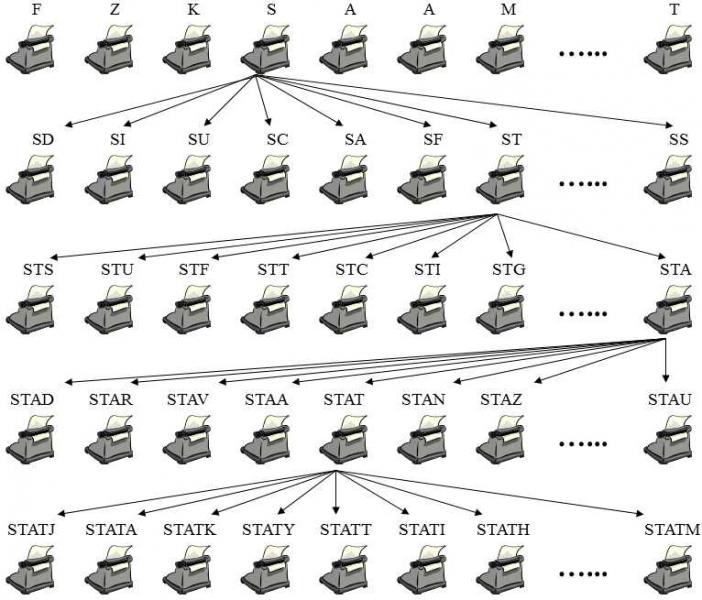
Fig. XXVII.1 Gradual formation of a complicated adaptive trait by natural selection. The probability that an ape will tap out the sentence “Taken statistically, it is impossible that something as complicated as an organism could be formed by a random process of evolution” on a typewriter is very low and a large herd of apes would require an unrealistically long time for this. However, such a single-step model of the formation of a complicated structure does not correspond to the assumed mechanism of the formation of complicated traits during biological evolution. If we wanted to model evolution using typewriters and apes, we would have to progress in individual steps. We would have to let the apes hit a key only once (analogous to the occurrence of one random mutation), then select, amongst the papers, the one with the right letter, here "T", (analogous to natural selection), copy it and insert it in all the typewriters (analogous to fixation of a suitable mutation) and have the apes press another key. Even with a not very numerous group of apes, this method would lead to the required sentence quite rapidly
there is only a negligible probability that any of them would write a sensible sentence within a reasonable period of time by only randomly pressing the keys, for example a sentence such as “Taken statistically, it is impossible that something as complicated as an organism could be formed by a random process of evolution.”.If, however, we have each ape press only one key, then send him back to the trees, we can find which of them wrote the letter “T”, copy this onto papers which we put in all the typewriters and request the apes to hit another key, etc. this sentence will be written with surprising speed.Darwin’s the theory of evolution assumes that random processes play an important role in the development of life, but not a decisive role.In the process of mutagenesis, random processes only generate the individual changes, from which the process of natural selection then non-randomly chooses those variants that improve the functioning of the whole system.
